Types of Blockchain & Smart Contracts Notes
In this article, we are going to learn about the three different types of blockchains & smart contracts. Bitcoin is one of the types of blockchain applications is known as the public. An important feature of smart contract implementation is that you do not need to use intermediary services such as brokers, notaries, agents etc. to conduct transactions.
In this article, we will cover the following topics.
- What Are the Different Types of Blockchain?
- Comparison of the public, consortium, and private blockchains.
- What is a Traditional Contract?
- What is Smart Contract?
- Why We Need Smart Contracts?
- Comparison of Smart Contracts and Traditional Contracts.
- How do smart contracts work?
- What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Smart Contracts?
Types of Blockchain
What Are the Different Types of Blockchain?
As you know, the impact of blockchain is changing very fast nowadays; It is difficult to understand why its effect is changing. Because new technology of transactions are being launched on a day to day basis. There are many areas in our industry where we can use this technology.
The easiest way to classify them is by type of blockchain; Bitcoin is one of the first types of blockchain is known as the public is permissionless. So we can say that public blockchain is truly decentralized in nature. Private or Federated blockchain is a Permissioned blockchain. Before we go and discuss the comparison between types of blockchain, we need to understand the difference between centralized, decentralized & distributed systems.
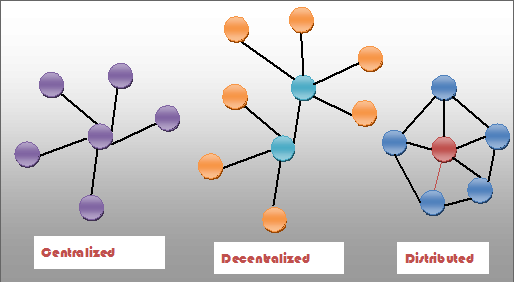
Write a difference between centralized, decentralized & distributed systems.
In Centralized systems, it controls all network of the system or it is created and controlled by a single entity whereas, in decentralized systems, every node makes it own decision. In the distributed system, jobs are distributed among several processors. So that the processors are interconnected to each other.
| key points | Centralized | Decentralized | Distributed |
| Databases | all the data in one server for use. | Entire database split in parts and distributed to different nodes for storage and use. | SOA-based systems |
| Fault tolerance | Low | Moderate | High |
| Maintenance | Low | Moderate | High |
| Scalability | Low | Moderate | High |
| Development | High | Moderate: | Moderate: |
| Evolution | Low | High | High |
| Example | Wikipedia | Bitcoin | Google, Facebook, Netflix, |
Types of blockchain are as follows.
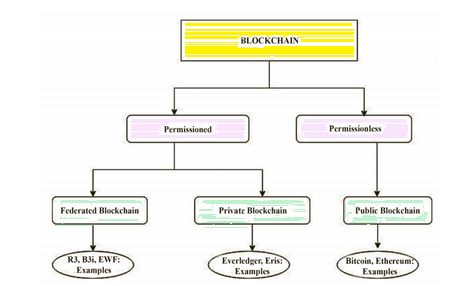
- Public blockchain or Permissionless
- Private blockchain or Permissioned
- Consortium or Federated or blockchain
Public Blockchain
It is Public in nature. Its network type is a decentralized and open network. Anyone anywhere in the world can download the protocol and read, write or participate in the network. No one in the central authority can control the blockchain. Furthermore, all data can be validated because once the data is written it cannot be changed, deleted, and modified. For examples of public blockchains include Bitcoin and Ethereum etc.
Private Blockchain
It is private in nature. Its network type is a centralized and closed network. It is an invitation-only network where participants require permission to read, write or audit the blockchain. It allows only specific users of the single organization to verify and add transaction blocks. However, everyone on the internet is generally allowed to view it. For examples of private blockchains include R3 (bank), Hyperledger, etc.
Consortium/Federated
It is similar to a private blockchain or permissioned, except that it is managed by multiple entities. Permission to verify, read and write of the blockchain controlled by a predetermined node. In a consortium blockchain, some aspects of the organizations are made public, while others remain private. For an example of Consortium Blockchain: Marco Polo, Energy Web Foundation, IBM Food Trust. etc.
Comparison of public, consortium and private blockchains
| Type | Public | Private | Consortium/Federated |
| Nature | Open | Closed | Controlled and closed |
| Access | Anyone can access | Single organization can access | Multiple Selected Organization can access |
| Transaction Speed | Slow | Lighter and Faster | Lighter and Faster |
| Network Type | Decentralized | Centralized | Semi-Decentralized |
| Approve | Anyone | Centralized | Few Members |
| Participants | Permission less, anonymous | Permissioned , Known Identities | Permissioned , Known Identities |
| Example | Bitcoin and Ethereum | R3 (bank), Hyperledger | Marco Polo, Energy Web Foundation, IBM Food Trust |
Smart Contracts
As you know, there are many big industries in the country that depend heavily on contracts, such as insurance, financial institutions, real estate, construction, entertainment, and law. If we use blockchain, then all industries will be benefited by this technology. Because by using this technology, you can update, manage, track and secure all your contracts without any dispute. Smart contracts, which are embedded with if / then statements and which do not require the involvement of the intermediary party to execute.
What is Traditional Contract?
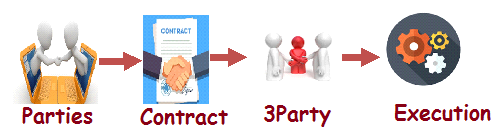
In this case, the two unknown parties X and Y are available and agreements between these two parties. So it is required intermediary or a third party to handle this situation and execute all processes.
What is smart Contracts?

In Smart contracts using Blockchain, no reliable intermediary is required to handle the transaction. Let’s take a example of buying and selling a house.
- If X wants to sell a house to Y, so in this case directly the transaction would be verified by each node in the Blockchain Network.
- If both parties agrees then Y automatically gets the access lock for the house. In this case Y as the new owner of the house.
- X will receives the amount directly from Y, without any middleman.
In this case blockchain will check all the information about the owner before selling and buying the house.
Why We Need Smart Contracts?
If we are use Smart Contracts, it will automate many solutions using Blockchain to make things simple and efficient. let’s compare how smart contracts are better than traditional contracts.
Comparison of Smart Contracts and Traditional Contracts
| Smart Contract | Traditional Contracts |
| self-executing computer program | legal terms |
| It cannot be modified or changed according to people’s | It are flexible and can be modified at any time |
| Work on the distributed ledger technology | Work on the institutional factors and requirements |
| It cannot be manipulated | It can be manipulated and changed easily |
| Readability difficult for human, but easy for machine | Readability easy for human |
| Easy to store | Difficult to store |
| Data extraction automatic | Data extraction possible but not easy |
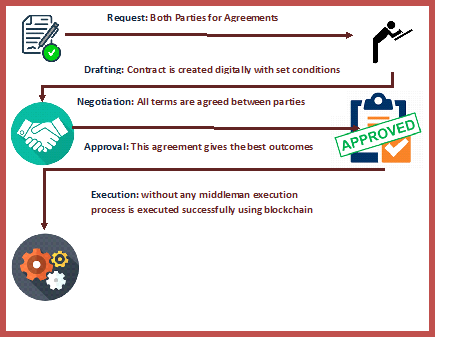
How do smart contracts work?
Ram is planning a trip to Goa and he wants to rent Amit’s house / apartment during this trip. But both parties depend on the third party because it will add to the agreement and terms between the two parties. In this case third party will take a charge fee from Ram and Amit for their service. If agreement is fail due to some reason, it will take a lot of time to solve this problem.
However, if Ram and Amit choose smart contract for the agreement, the contract will follow logical behavioral patterns and will ensure that the agreement’s terms are fulfilled. The parties can write all possibility into the blockchain smart contract and the contract will automatically implement. For example, if Amit give wrong address then Ram gets a refund of his rent payment; or if Ram cancels his trip then Amit receives the damaged payment and Ram is entitled for remainder amount paid by him. Because of the immutable nature of smart contracts, neither party could cheat or default on the agreement. Due to the irreversible nature of smart contracts, neither party could cheat nor default on the agreement.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Smart Contracts?
Smart Contracts Advantages and Disadvantages are following
Advantages of Smart Contracts are following
- Safety: data in the decentralized form cannot be lost or changed without your permission.
- Most processes are automated and eliminate the risks frequently observed in traditional contracts.
- Total Transparency: Transparent between two (or more) parties. If anyone has to make any changes to the terms and conditions, then they have to decide it before the contract is ready.
- Accuracy: It increases accuracy because the manual errors are eliminated.
- There is no need to rely on a broker, lawyer, or other intermediaries to confirm any agreement. It also reduces intermediate costs.
- Reduction in time spent on processing documents.
Disadvantage of Smart Contracts are following
- Lack of understanding: The consumers are not aware of this new technology and they do not understand it yet.
- Cost increases: Software still requires more maintenance.
- Uncertain legal status: Smart contracts are clearly not regulated by any government, a reality that may change.
- The dependence on oracles makes smart contracts vulnerable to abuse.
- Greater flexibility creates a larger attack surface.
