JEE (Main) – Number System Notes
JEE (Main) – Notes of Number System
- In the early days, there were no instruments while counting, people used to count the numbers with the help of stones, sticks, etc.
- These methods were not sufficient and had many limitations.
- We talk about the number of people coming to school, the number of modules taken per student, etc.
- Since our childhood, we have studied numbers (1,2,3,…), and arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of numbers.
- Numbers play a great role in various activities.
Number System:
The number system is a set of numbers in which one number is related to another number using one or more algebraic operations. There are different number systems which are as follows:
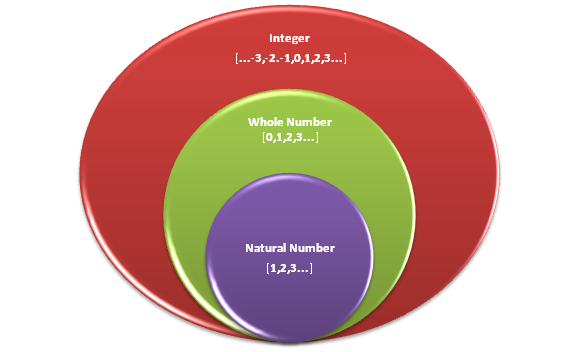
- Natural Numbers
- Whole Number
- Integer
1. Natural Numbers
- The natural (or counting) numbers are {1,2,3,4,5,…… N}.
- These numbers are also called Positive Numbers.
- In this case, counting starts from 1 and contains infinitely many natural numbers.
- Set of Natural numbers is represented by N = {1,2,3,4,5,…… }.
- Even Natural Number: Exactly divisible by 2 and infinitely many even numbers.
- Set of Even Natural numbers are {2,4,6,8,…… }.
- Odd Natural Number: Not exactly divisible by 2 and infinitely many odd numbers.
- Set of Odd Natural numbers are {1,3,5,7,…… }.
2. Whole Numbers
- The numbers which start from zero (0) are called whole numbers.
- In other words, whole numbers are the natural numbers together with 0.
- Whole Numbers are simply the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, … (and so on).
- Set of whole numbers is represented by W = {1,2,3,4,5,…… }.
3. Integers
- Integers are the collection of whole numbers and negative numbers.
- The numbers. …… -5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3, +4, +5, +6, + 7 …. etc.
- Integers do not include fraction numbers.
- Integers are represented by the symbol Z= {…… -5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3, +4, +5,….}.
- The sum, product, and difference of any two integers is also an integer. But this is not true for the division.
- Positive Integer: Set of positive numbers is represented by Z+ = {1,2,3,4,5,…… }.
- Negative Integer: Set of negative numbers is represented by Z– = {-1,-2,-3,-4,-5,…… }.
- Integers can be zero {0}.
- Non-Negative Integers = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, … } = W
- Non-Positive Integers = { 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, … }
- Even Numbers – n / 2 = 0 where n is counting number; [0,2,4,…]
- Odd Numbers – n / 2 ≠ 0 where n is counting number; [1,3,5,…]
4. Prime Number
- It is a whole number that is greater than 1.
- It is divisible only by itself or 1.
- Set of prime numbers is {2,3,5,7,11,13,17…… }.
5. Composite Number
- It is the opposite of Prime numbers.
- It can be divided exactly by a whole number other than itself.
- The number except 1 and which are not prime.
- A composite number is a number with more than 2 factors.
- Example: Factor 8 are = 1, 2, 4, 8
6. Co-Primes Numbers
- Two natural numbers are co-primes if their H.C.F. is 1.
- Two consecutive natural numbers are always co-prime.
- Co-prime numbers are also known as relatively prime or mutually prime numbers.
- Example 1: For 21 and 22 :
- The factors of 21 are 1, 3, 7, and 21.
- The factors of 22 are 1, 2, 11, and 22.
- Here 21 and 22 have only one common factor that is 1. Hence, their HCF is 1 and is co-prime.
Recommended Reading
Trigonometric identities and equations
