Block chain Technology: Understanding Block chain for Enterprises: Notes
| Synchronous Consensus |
They are exist various time of type of consensus algorithms:
- Paxos
- Raft
- Byzantine fault tolerance
Paxos
- Paxos is a family of protocols for solving consensus in a network of unreliable processors.
- The Paxos protocol was first published in 1989 and named after a fictional legislative consensus system used on the Paxos island in Greece.
- Paxos is usually used where durability is required in which the amount of durable state could be large.e.g. to replicate a file or a database
- The protocol attempts to make progress even during periods when some bounded number of replicas are unresponsive.
- There is also a mechanism to drop a permanently failed replica or to add a new replica.
Paxos – assumptions
- Processors
- Processors operate at arbitrary speed.
- Processors may experience failures.
- Processors with stable storage may re-join the protocol after failures.
- Processors do not collude, lie, or otherwise attempt to subvert the protocol.
Network
- Processors can send messages to any other processor.
- Messages are sent asynchronously and may take arbitrarily long to deliver.
- Messages may be lost, reordered, or duplicated.
- Messages are delivered without corruption.
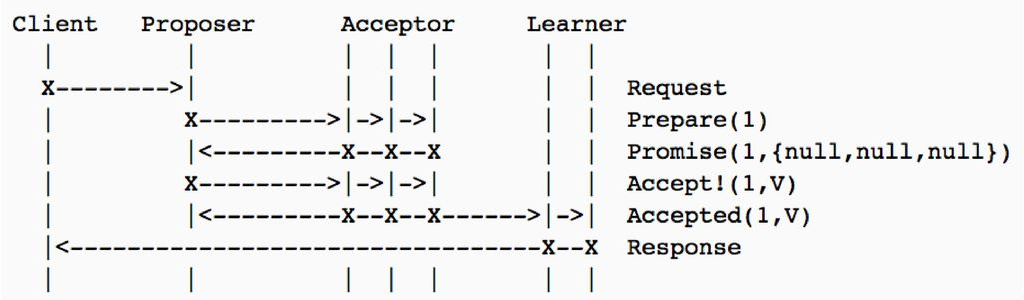
Paxos – roles
Client: The Client issues a request to the distributed system, and waits for a response. For instance, a write request on a file in a distributed file server.
Acceptor (Voter): The Acceptors act as the fault-tolerant “memory” of the protocol. Acceptors are collected into groups called Quorums. Any message sent to an Acceptor must be sent to a Quorum of Acceptors. Any message received from an Acceptor is ignored unless a copy is received from each Acceptor in a Quorum.
Proposer: A Proposer advocates a client request, attempting to convince the Acceptors to agree on it, and acting as a coordinator to move the protocol forward when conflicts occur.
Learner: Learners act as the replication factor for the protocol. Once a Client request has been agreed on by the Acceptors, the Learner may take action
Leader: Paxos requires a distinguished Proposer (called the leader) to make progress.
- Many processes may believe they are leaders, but the protocol only guarantees progress if one of them is eventually chosen.
- If two processes believe they are leaders, they may stall the protocol by continuously proposing conflicting updates.
- However, the safety properties are still preserved in that case.
In most deployments of Paxos, each participating process acts in three roles; Proposer, Acceptor and Learner
PAXOS – safety properties
Safety
- Only a value that has been proposed may be chosen.
- Only a single value is chosen.
- A node never learns that a value has been chosen unless it actually has been.
Liveness
- Some proposed value is eventually chosen.
- If a value has been chosen, a node can eventually learn the value.
PAXOS Algorithm Phase 1 (prepare):
- A proposer selects a proposal number n and sends a prepare request with number n to majority of acceptors.
- If an acceptor receives a prepare request with number n greater than that of any prepare request it saw, it responses YES to that request with a promise not to accept any more proposals numbered less than n and include the highest-numbered proposal (if any) that it has accepted.
PAXOS Algorithm Phase 2 (accept):
- If the proposer receives a response YES to its prepare requests from a majority of acceptors, then it sends an accept request to each of those acceptors for a proposal numbered n with a values v which is the value of the highest-numbered proposal among the responses.
- If an acceptor receives an accept request for a proposal numbered n, it accepts the proposal unless it has already responded to a prepare request having a number greater than n.
PAXOS Applications
Google, Chubby lock service. IBM SAN Amazon
Petal: Distributed virtual disks.
Frangipani: A scalable distributed file system.
Paxos: basic message flow