Introduction of Blockchain (Notes)
Introduction of Blockchain: We have been listening to the word bitcoin for a long time. People have many questions in their minds about Bitcoin like what is Bitcoin?. What do people benefit from Bitcoin?. How it works. As you know, the price of Bitcoin is increasing day by day. But do you know what is the technology behind Bitcoin?.
So we can say that Blockchain technology will completely transform our IT industry as open-source software did a decade ago.
Similarly, Blockchain is also going to be the best way to share information in the coming times. Blockchain costs will be low and can be easily implemented between open and private networks.
So we have to first understand Blockchain Technology completely, and what are the benefits of Blockchain Technology.
Contents of the Article.
- What is a Blockchain?.
- Why we need blockchain?.
- What Blockchain is NOT!.
- Explain the Blockchain Architecture.
- What is a brief history of blockchain?.
What is a Blockchain?
We will discuss various definition of BlockChain:
Definition 1.
Blockchain is apparently a clever imagination- it was invented by Satoshi Nakamoto. Blockchain is a chain of blocks that contains information.
Each block records all recent transactions, and once completed it moves to the blockchain as a permanent database. The block is completed each time, a new block is generated.
Definition 2.
A blockchain is a constantly growing ledger that keeps a permanent record of all the transactions that have taken place in a secure, chronological, and immutable way.
Let’s explain the definition.
- Ledger: It is a file that is constantly growing.
- Permanent: It means once the transaction goes inside a blockchain, you can put up it permanently in the ledger.
- Secure: it placed information in a secure way. It uses very advanced cryptography to make sure that the information is locked inside the blockchain.
- Chronological: Chronological means every transaction happens after the previous one.
- Immutable: If you build all the transactions onto the blockchain, this ledger can never be changed.
What Blockchain is NOT!

- Blockchain technology and Bitcoin have no commonality. Both are on the banks of the river.
- Blockchain is not Bitcoin, but it is the technology behind Bitcoin.
- Bitcoin is a digital medium through which we can buy and sell.
- Blockchain is a digital ledger where not only a digital currency but anything can be digitally placed and recorded.
- You can’t have Bitcoin without blockchain, but you can have a blockchain without Bitcoin.
Explain the Blockchain Architecture.
let’s discuss the architecture of Blockchain. Its key components have been normalized and then modified by various companies. It is leading to various blockchain projects such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, Hyperledger, etc. Therefore, we will discuss blockchain architecture.
What is a Block?
Various stages of transactions generate a set of data called blocks. Blocks are associated with a greater number of transactions, forming a chain, hence a name block. Encryption software never assures anyone to remove or change the block.
For example, a bitcoin block contains information about the sender, receiver, number of bitcoins.

The first block in the chain is known as the Genesis block. Each new block in the chain is connected to the previous block.
A block has mainly 6 parts:

- Index: Show Position of the block in blockchain
- Data: Data stored on the node
- Hash : Unique ID of block.
- Previous Hash: Hash of previous block. But in case of genesis block, this value is 0.
- Time stamp: The time when that particular block was created.
- Nonce: It is a number used to find a valid hash.
Mechanism of Blockchain.
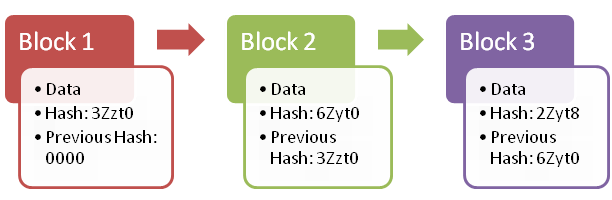
Consider the following example, where we have a take chain of 3 blocks. The first block has no predecessor. Hence, it does not contain has the previous block. The second Block contains the previous hash (3Zzt0) of the first Block. the same as the third Block contains the previous hash (6Zyt0) of the second Block.
Hence, all blocks are containing hashes of previous blocks. This is the technique that makes a blockchain so secure.
Why we need blockchain?
- Bring Trust : To establish trust between ourselves, we depend on individual third parties such as banks, land registries, government etc.
- Decentralization: To Chances of error, mistakes and corruption can happen in centralized control systems.
- Remove Middle Man : They always comes with somewhat risk and cost.
What is a brief history of blockchain?
- 1990: The blockchain began in the 1990s with Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta. How to protect the past and maintain digital information safe and resistant to tampering.
- 1991: Further work on the cryptographically secured chain of blocks was described by Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta.
- 1992: Haber, Stornetta, and Dave Bayer incorporated Merkle trees into the design, which improved its efficiency by allowing several document certificates to be collected into one block.
- 2008-2009: Bitcoin is born. Satoshi Nakamoto released a white paper “Bitcoin: A peer to peer electronic cash system” and implements the first blockchain as the public ledger for transactions made using bitcoin
- 2014: start of Blockchain 2.0, the second-generation blockchain technology with a new application (e.g. intellectual property, social inequality). Blockchain technology is separated from the currency and its potential for other financial, inter-organisational transactions is explored. Blockchain 2.0 is born, referring to applications beyond currency.
- 2015: The Ethereum blockchain system introduces computer programs into the blocks, representing financial instruments such as bonds. These become known as smart contracts.
Summary
- Blockchain is also going to be the best way to share information in the coming times.
- A blockchain is a constantly growing ledger that keeps a permanent record of all the transactions that have taken place in a secure, chronological, and immutable way.
- Blockchain technology and Bitcoin have no commonality. Both are on the banks of the river.
- Various stages of transactions generate a set of data called blocks.
